Were you assigned to work on the MEAN Stack? Did your organization choose MongoDB for data storage? As a beginner in MongoDB, it is important to familiarize yourself with data modeling in MongoDB.
One of the major considerations for data modeling in MongoDB is to assess the DB engine’s performance, balance the requirements of the application, and think about the retrieval patterns. As a beginner in MongoDB, think about how your application works with queries and updates and processes data.
MongoDB Schema
The schema of MongoDB’s NoSQL is considerably different from the relational and SQL databases. In the latter, you have to design and specify the schema of a table before you can begin with the insert operations to populate the table. There is no such thing in MongoDB.
The collections used by MongoDB operate on a different strategy which means that it is not necessary that two documents (similar to rows in SQL databases) can have the same schema. As a result, it is not mandatory for a document in a collection to adhere to the same data types and fields.
If you must create fields in the document or you have to modify the current fields, then you have to update a new structure for the document.
How to Improve Data Modeling
During data modeling in MongoDB, you must analyze your data and queries and consider the following tips.
Capped Collections
Think about how your application is going to take advantage of the database. For instance, if your application is going to use too many insert operations, then you can benefit from the use of capped collections.
Manage Growing Documents
Write operations increase data exponentially like when an array is updated with new fields, the data increases quickly. It can be a good practice to keep a track of the growth of your documents for data modeling.
Assessing Atomicity
On the document level, the operations in MongoDB are strictly atomic. A single write operation can only change the contents of a single document. There are some write operations that can modify multiple documents, but behind the scenes, they only process one document at a time. Therefore, you have to ensure that you are able to factor in accurate atomic dependency according to your requirements.
The use of embedded data models is often recommended to utilize atomic operations. If you use references, then your application is forced in working with different read/write operations.
When to Use Sharding?
Sharding is an excellent option for horizontal scaling. It can be advantageous when you have to deploy datasets in a large amount of data and where there is a major need for read and write operations. Sharding helps in categorizing database collections. This helps in the efficient utilization for the documents of the collection.
To manage and distribute data in MongoDB, you are required to create a shared key. Shard key has to be carefully selected or it may have an adverse impact on the application’s performance. Likewise, the right shard key can be used to prevent a query’s isolation. Other advantages include a notable uplift in the write capacity. It is imperative that you take your time to select a field for the position of shard key.
When to Use Indexes?
The first option to improve the query performance in MongoDB is an index. To consider the use of an index, go through all your queries. Look for those fields which are repeated the most often. Make a list of these queries and use them for your indexes. As a result, you can begin to notice a considerable improvement in the performance of your queries. Bear in mind, that indexes consume space both in the RAM and hard disk. Hence, you have to keep these factors in mind while creating indexes or your strategy can backfire instead.
Limit the Number of Collections
Sometimes, it is necessary to use different collections based on application requirements. However, at times, you may have used two collections when it may have been possible to do your work through a single one. Since each collection comes with its own overhead, hence you cannot overuse them.
Optimize Small Document in Collections
In case, you have single or multiple collections where you can notice a large number of small documents, then you can achieve a greater degree of performance by using the embedded data model. To increase a small document into a larger one via roll-up, you can try to see if it is possible to design a logical relationship between them during grouping.
Each document in MongoDB comes up with its own overhead. The overhead for a single document may not be much but multiple documents can make matters worse for your application. To optimize your collections, you can use these techniques.
- If you have worked with MongoDB then you would have noticed that it automatically creates an “_id” field for each document and adds a unique 12-byte “ObjectId”. MongoDB indexes the “_id” field. However, this indexing may waste storage. To optimize your collection, modify “_id” field’s value when you create a new document. What this does is that it helps to save a value which could have been assigned to another document. While there is no explicit restriction to use a value for the “_id” field but do not forget the fact that it is used as a primary key in MongoDB. Hence, your value must be unique.
- MongoDB documents store the name of all fields which does not bode well for small documents. In small documents, a large portion of their size can be dictated due to the number of their fields. Therefore, what you can do is that make sure that you use small and relevant names for fields. For instance, if there is the following field.
father_name: “Martin”
Then you can change it by writing the following.
f_name : “Martin”
At first glance, you may have only reduced 5 letters but for the application, you have decreased a significant number of bytes which are used to represent the field. When you will do the same for all queries then it can make a noticeable difference.
Let’s see how this works with an example
The major choice which you have to think around while working for data modeling in MongoDB is what does your DOCUMENT structure entail? You have to decide what the relationships which represent your data are like whether you are dealing with a one-to-one relationship or a one-to-many relationship. In order to do this, you have two strategies.
Embedded Data Models
MongoDB allows you to “embed” similar data in the same document. The alternative term for embedded data models is de-normalized models. Consider the following format for embedded data models. In this example, the document begins with two standard fields “_id” and “name” to represent the details of a user. However, for contact information and residence, one field is not enough to store data as there are more than one attributes for data. Therefore, you can use the embedded data model to add a document within a document. For “contact_information” curly brackets are used to change the field to a document and add “email_address” and “office_phone”. A similar technique is applied to the residence of the user.
{
_id: “abc”,
name: “Bruce Wayne”,
contact_information: {
email_address: “bruce@ittechbook.com”,
office_phone: ” (123) 456–7890″,
},
residence: {
country: “USA”,
city: “Bothell”,
}
}
The strategy to store similar types of data in the same document is useful for a reason; they limit the number of queries to execute standard operations. However, the questions which might be going around in your mind is, when is the correct time to use an embedded data model? There are two scenarios which can be marked as appropriate for the use of embedded data models.
Firstly, whenever you find a one-to-many relationship in an entity, then it would be wise to infuse embedding. Secondly, whenever you identify an entity with “contains” relationship, then it is also a good time to use this data model. In embedded documents, you can access information by using the dot notation.
One-to-Many Relationship with Embedding
One-to-many is a common type of database relationship where a collection A can match multiple documents in collection B but the latter can only match for one document in A.
Consider the following example to see when de-normalized data models hold an advantage over normalized data models. To select one, you have to consider the growth of documents, access frequency, and similar factors.
In this example, reference is using three examples.
{
_id: “barney”,
name: “Barney Peters”
}
{
user_id: “Barney”,
street: “824 XYZ”,
city: “Baltimore”,
state: “MD”,
zip: “xxxxx”
}
{
user_id: “Barney”,
street: “454 XYZ”,
city: “Boston”,
state: “MA”,
zip: “xxxx”
}
If you can see closely, then it is obvious that the application has to continuously retrieve data for address along with other field names which are not required. As a result, several queries are wasted.
On the other hand, embedding your address field can ensure that the efficiency of your application is boosted and your application will only require a single query.
{
_id: “barney”,
name: “Barney Peters”,
addresses: [
{
user_id: “barney”,
street: “763 UIO Street”,
city: “Baltimore”,
state: “MD”,
zip: “xxxxx”
},
{
user_id: “barney”,
street: “102 JK Street”,
city: “Boston”,
state: “MA”,
zip: “xxxxx”
}
]
}
Normalized Data models (References)
In normalized data models, you can utilize references to represent relationship between multiple documents. To understand references, consider the following diagram.
References or normalized data models are used in the cases of one-to-many relationship models and many-to-many relationship models. In some instances of embedded documents model, we might have to repeat some data which could be avoided by using references. For example, see the following example.
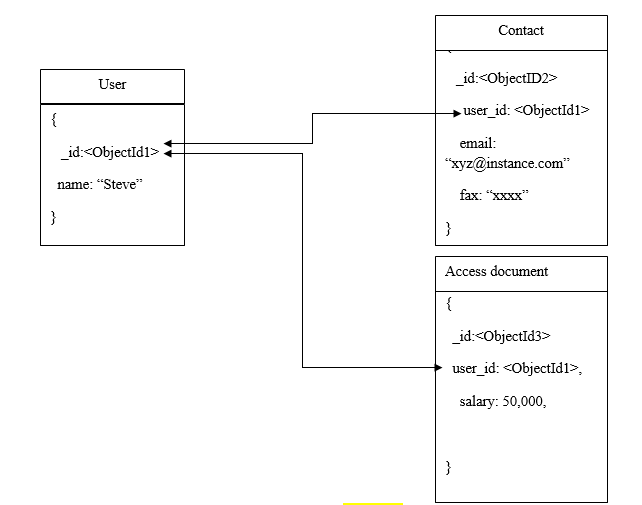
In this example, the “_id” field in the user document references to two other documents that are required to use the same field.
References are suitable for datasets which are based on hierarchy. They can be used to describe multiple many-to-many relationships.
While references provide a greater level of flexibility in comparison to embedding, they also require the applications to issue the suitable follow-up queries for their resolution. Put simply, references can increase the processing between the client-side application and the server.
One-to-Many Relationship with References
There are some cases in which a one-to-many relationship is better off with references rather than embedding. In these scenarios, embedding can cause needless repetition.
{
title: “MongoDB Guide”,
author: [ “Mike Jones”, “Robert Johnson” ],
published_date: ISODate(“2019-1-1”),
pages: 1,200,
language: “English”,
publisher: {
name: “ASD Publishers”,
founded: 2009,
location: “San Francisco”
}
}
{
title: “Java for Beginners”,
author: “Randall James”,
published_date: ISODate(“2019-01-02”),
pages: 800,
language: “English”,
publisher: {
name: “BNM Publishers”,
founded: 2005,
location: “San Francisco”
}
}
As you can realize whenever a query requires the information of a publisher, that information is repeated continuously. By leveraging references, you can improve your performance by storing the information of the publisher in a different collection. In cases, where a single book has limited publishers and the likelihood of their growth is low, references can make a good impact. For instance,
{
name: “ASD Publishers”,
founded: 2009,
location: “San Francisco”
books: [101, 102, …]
}
{
_id: 101
title: “MongoDB Guide”,
author: [ “Mike Jones”, “Robert Johnson” ],
published_date: ISODate(“2019-1-1”),
pages: 1,200,
language: “English }
{
_id: 102
title: “Java for Beginners”,
author: “Randall James”,
published_date: ISODate(“2019-01-02”),
pages: 800,
language: “English”,
}